PIELDS ENGINEERING
Secondary Battery Na₂SO₄ Wastewater Treatment Methods
Secondary Battery High-Concentration Na₂SO₄Wastewater Treatment Process
The hydrometallurgical process is widely applied in the secondary battery industry, primarily using sulfuric acid, which requires 18 to 20 times more industrial
water compared to the general manufacturing industry.
Additionally, the smelting process, which involves the use of caustic soda, produces a salt component known as sodium sulfate (Na₂SO₄).
The resulting contaminated water discharged by the processing company is commonly known as Na₂SO₄ wastewater.
Commercially viable desalination technologies for treating high-concentration Na₂SO₄ wastewater from the secondary battery industry include thermal
techniques, ion exchange, and membrane techniques. Their respective pros and cons are outlined below.
| Sortation | Thermal Techniques | Ion Exchange | Membrane Techniques |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pros |
|
|
|
| Cons |
|
|
|
| Charact eristics |
|
|
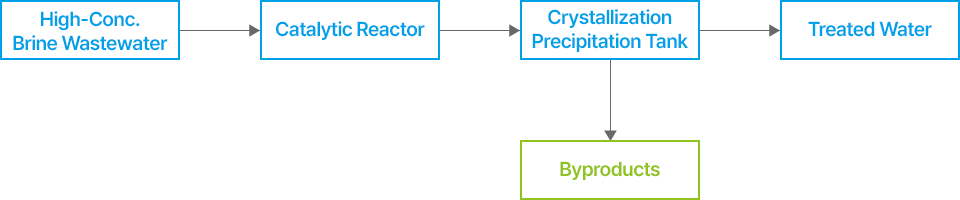
KARI's technology removes heavy metals from highly concentrated brine wastewater generated during the production of secondary battery electrode
materials through catalysis. It also enables the removal of salts via crystallization to produce clean treated water with an ecotoxicity level of 1 or less,
which is then recycled for industrial use. Additionally, the byproducts are recovered and recycled from the brine wastewater.
The process is as follows:
Pields Engineering and KARI have signed an agreement to collaborate on the brine wastewater treatment facility project,
leveraging eco-friendly technologies focused on 'the utilization of wastewater resources.’
This collaboration project will utilize Pields Engineering's technical services, EPC capabilities, and experienced personnel.
Technical Services from Pields Engineering
-

step1
Process Design
-

step2
Factory Renovations
-

step3
Feasibility Studies
-

step4
Commissioning Support
Benefits of Pields Engineering
- Minimizes the overall project schedule through the quick application of a proven design package that covers everything from basic design to material supply and construction, leveraging experience as an EPC veteran in Green New Deal projects.
- The rapid deployment of experienced personnel and the use of standardized designs, materials, and construction methods helps reduce costs and time.
- Has extensive experience in designing and constructing facilities for producers of large-scale secondary battery anode material precursors.

