PIELDS ENGINEERING
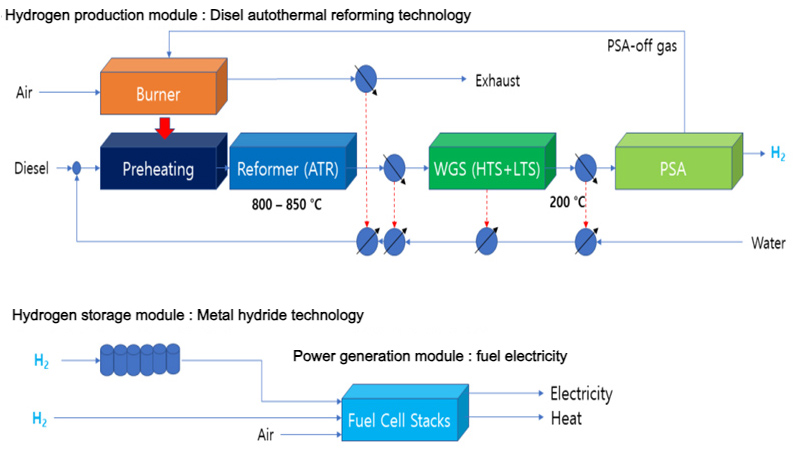
Hydrogen Production Facilities
Electrolysis Method
Electrolysis of water is the process of breaking down water (H₂O) into hydrogen (H₂) and oxygen (O₂) using electrical energy.
It is a clean method for producing hydrogen, especially when combined with renewable energy sources (e.g., solar and wind), making it nearly carbon-free.
This method offers the advantages of zero carbon emissions, production of high-purity hydrogen, and applicability to a wide range of locations and scales.
Electrolysis Reactions
The reactions that take place inside the electrolyzer are as follows:
Cathodic Reactions (Reduction Reactions) : 2H_2 O+2e^-→H_2 +2OH^-
Anodic Reactions (Oxidation Reactions) : 4OH^-→2H_2 O+O_2 +4e^-
Methods of electrolysis
Alkaline Electrolysis : This method uses an aqueous solution of potassium hydroxide (KOH) or sodium hydroxide (NaOH) as the electrolyte.
The method is relatively inexpensive and durable, but can be less power-efficient.
Proton Exchange Membrane Electrolysis (PEM) : A solid polymer membrane (PEM) is used as the electrolyte.
This method offers high efficiency and generates high-purity hydrogen, but is relatively expensive.
Solid Oxide Electrolysis (SOE) : This method operates at high temperatures (around 700–1000°C) and uses solid oxide as the electrolyte.
This method is highly efficient but presents durability issues at high temperatures.
Technical Services from Pields Engineering
-

step1
Process Design
(Basic & Detailed) -

step2
Technical Consulting for
Factory Optimization and
Performance Improvement -

step3
Factory
Renovations -
step4
Maintenance
-

step5
Feasibility Studies
-

step6
Commissioning Support
Benefits of Pields Engineering
- Provides basic design services as part of an EPC package.
- Reduces costs and time based on in-house expertise in process, mechanical, electrical, and control design, as well as construction experience.
- Experienced in securing key package vendors and collaborating on EPC work.
- Experienced in conducting R&D for modular and mobile hydrogen production, storage, delivery, and power supply systems using electrolysis methods.
- Has experience working on projects across a variety of hydrogen-related fields.
- Reduces costs and time with the rapid response of experienced personnel.

